Leakage is defined as uncontrolled entry or exit of fluid from a hole or crack in the system or from several connection parts of the system. The leak rate depends on several factors such as the size of hole/holes, gas type, the pressure difference between the inside and the outside of the system. The detection and elimination of leaks is extremely important for a number of reasons, including:
• Operator safety (egression of toxic gases/fluids)
• Product safety (if air enters a system, it may significantly contribute the formation of an explosive mixture, which should be prevented.)
• To ensure a long user-life product
• To satisfy and maintain pressure/vacuum
• For process efficiency
• For environmental and quality standards
• Reducing Costs
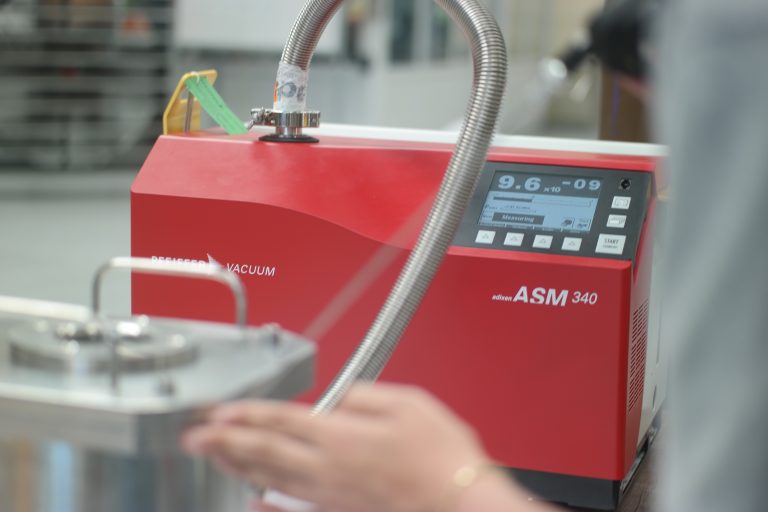
A test using helium as tracer gas is called ‘Helium Leak Test’. Helium test can be used to determine the leakage rates from 1*10-6 mbar*lt/s to 1*10-12 mbar*lt/s.
Helium Leak Test can be performed in two ways. While the first of these is the “Vacuum Method”, the other is the “Sniffer Method”
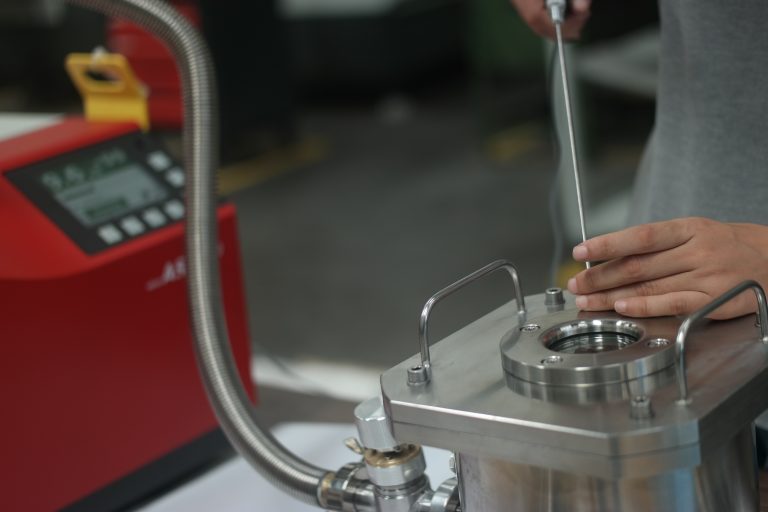
– In the vacuum method process, the inside of the part to be tested is vacuumed and helium gas is sprayed with a sprayer to the points where there may be leakage from the outside (i.e. welded areas, flanges, portals, connection points, etc.). Helium gas entering the vacuumed test piece from the leakage zones is sent to the mass spectrometer for recording.
– In the method we call the sniffer method, the inside of the tested part is pressurized to a certain level with helium gas. After this process, the possible leakage points are scanned with the help of a sniffer and it is determined whether there is any leakage. Helium gas detected by the sniffer is sent to the mass spectrometer for recording.
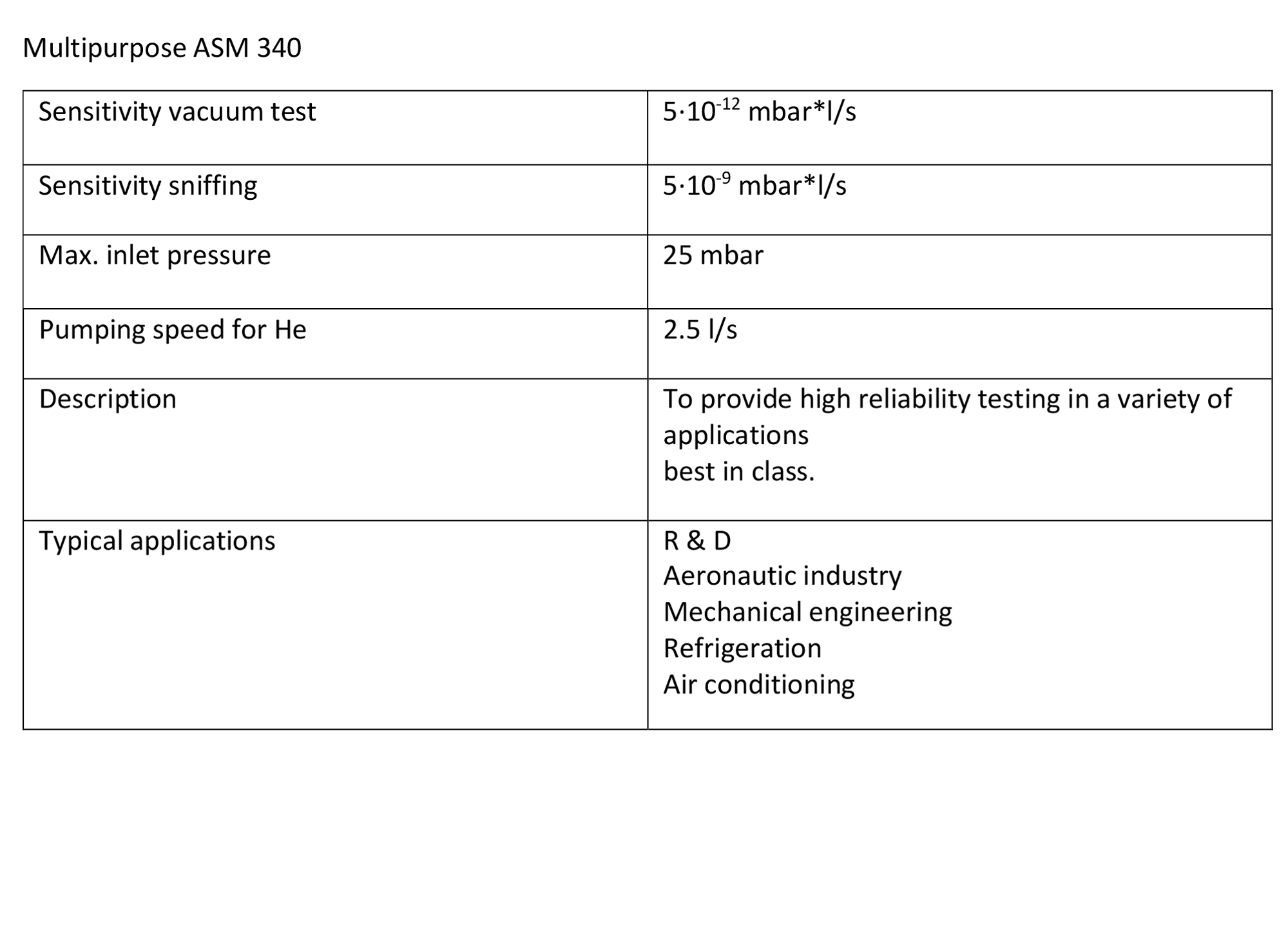
For the Helium Leak Test service provided by our company, Multipurpose ASM 340 of Pfeiffer Vacuum Company is used.